树
树
树与数组链表的比较
数组存储方式的分析
- 优点:通过下标访问元素,速度快。对于有序数组,还可以使用二分查找提高检索速度
- 缺点: 如果要检索具体某个值,或者插入值,会整体移动,效率低
链式存储方式的分析
- 优点:插入,删除效率较高
- 缺点:检索效率低
树存储方式分析
提高数据存储,读取的效率,比如利用二叉排序树,即保证了数据查询的效率,也保证了数据修改,插入,删除的效率
二叉树
- 每个节点最多只有两个子节点的一种形式称为二叉树
- 二叉树的子节点分为左节点和右节点
- 如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层,并且节点总数 2^n-1 n 为层数,则我们称为满二叉树
- 如果该二叉树所有叶子节点都在最后一层或者倒数第二次,而且最后一层的叶子节点在左边连续,倒数第二层的叶子节点在右边连续,我们称为完全二叉树
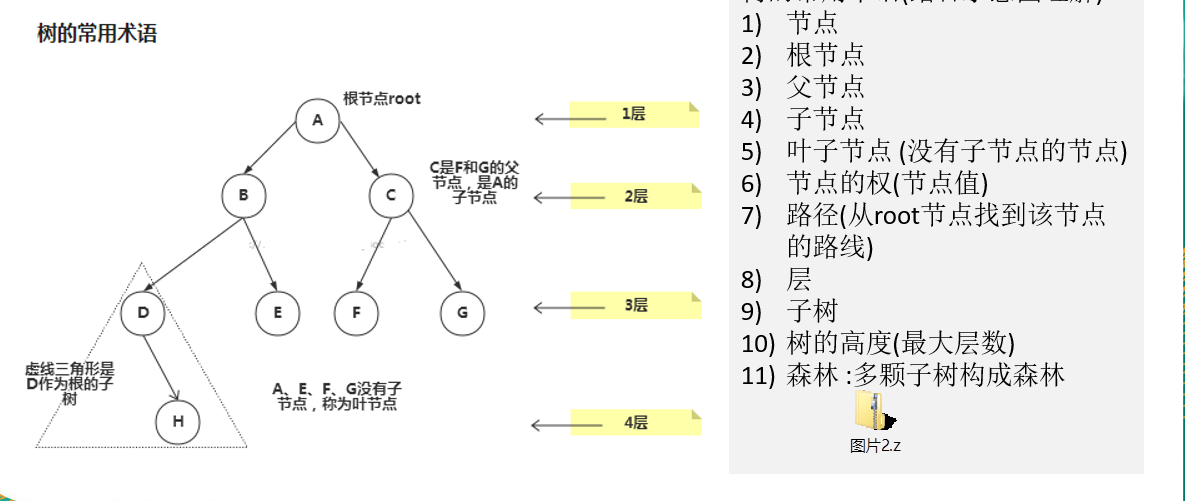
相关概念
- 节点
- 根节点
- 父节点
- 子节点
- 叶子节点(没有子节点)
- 节点的权
- 路径(从 root 节点找到该节点的路线)
- 层
- 子树
- 树的高度(最大层数)
- 森林(多颗子树构成森林)
遍历
二叉树遍历(父节点输出位置对应了 前序 中序 后序 ,左子树始终比右子树先输出)
- 前序遍历: 先输出父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树
- 中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再输出父节点,再遍历右子树
- 后续遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后输出父节点
查询与删除遍历类似
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HeroTree heroTree = new HeroTree();
//创建需要的结点
HeroTreeNode root = new HeroTreeNode(1, "宋江");
HeroTreeNode node2 = new HeroTreeNode(2, "吴用");
HeroTreeNode node3 = new HeroTreeNode(3, "卢俊义");
HeroTreeNode node4 = new HeroTreeNode(4, "林冲");
HeroTreeNode node5 = new HeroTreeNode(5, "关胜");
//说明,我们先手动创建该二叉树,后面我们学习递归的方式创建二叉树
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node3.setRight(node4);
node3.setLeft(node5);
heroTree.setRoot(root);
heroTree.DelNode(2);
//测试
System.out.println("前序遍历"); // 1,2,3,5,4
heroTree.preOrder();
//
// //测试
// System.out.println("中序遍历");
// heroTree.midOrder(); // 2,1,5,3,4
//
// System.out.println("后序遍历");
// heroTree.postOrder(); // 2,5,4,3,1
// HeroTreeNode node = heroTree.PostSearch(5);
// if(node!=null)
// {
// node.ToString();
// }else {
// System.out.println("target node is null");
// }
}
}
class HeroTree{
HeroTreeNode root;
public void setRoot(HeroTreeNode root)
{
this.root=root;
}
public void preOrder()
{
if(root!=null)
{
root.PreOrder();
}
}
public void midOrder()
{
if(root!=null)
{
root.MiddleOrder();
}
}
public void postOrder()
{
if(root!=null)
{
root.PostOrder();
}
}
//
public HeroTreeNode PreSearch(int id)
{
if(root!=null)
{
return root.PreSearch(id);
}
return null;
}
public HeroTreeNode MidSearch(int id)
{
if(root!=null)
{
return root.MidSearch(id);
}
return null;
}
public HeroTreeNode PostSearch(int id)
{
if(root!=null)
{
return root.PostSearch(id);
}
return null;
}
//删除节点
/**
* 1.如果是root则置空
* 2.判断左子节点是否是目标
* 3.判断右子节点是否是目标
* 4.1-3不满足,则递归左子节点
* 5.1-4不满足,则递归右子节点
* @param id 待删除节点
*/
public void DelNode(int id)
{
if(root==null)
{
return;
}
DelNode(root,id);
}
//删除节点
void DelNode(HeroTreeNode node,int id)
{
if(node.id==id)
{
node=null;
return;
}else if(node.left!=null && node.left.id==id)
{
node.left=null;
return;
}else if(node.right!=null&&node.right.id==id)
{
node.right=null;
return;
}
if(node.left!=null)
{
DelNode(node.left,id);
}
if(node.right!=null)
{
DelNode(node.right,id);
}
}
}
class HeroTreeNode{
public int id;
public String name;
//左子节点
HeroTreeNode left;
//右子几点
HeroTreeNode right;
public void setLeft(HeroTreeNode node)
{left=node;}
public void setRight(HeroTreeNode node)
{
right=node;
}
public HeroTreeNode(int id,String name)
{
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
}
public void ToString()
{
System.out.println("id:"+id+" name:"+name);
}
/**
* 前序遍历 根节点 左节点 右节点
*/
public void PreOrder()
{
this.ToString();
if(left!=null)
{
left.PreOrder();
}
if(right!=null)
{
right.PreOrder();
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历 左节点 根节点 右节点
*/
public void MiddleOrder()
{
if(left!=null)
{
left.MiddleOrder();
}
this.ToString();
if(right!=null)
{
right.MiddleOrder();
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历 左节点 右节点 根节点
*/
public void PostOrder()
{
if(left!=null)
{
left.PostOrder();
}
if(right!=null)
{
right.PostOrder();
}
this.ToString();
}
public HeroTreeNode PreSearch(int id)
{
System.out.println("PreSearch");
if(this.id==id)
{
return this;
}
HeroTreeNode node=null;
if(left!=null)
{
node = left.PreSearch(id);
}
if(node!=null)
{
return node;
}
if(right!=null)
{
node= right.PreSearch(id);
}
return node;
}
public HeroTreeNode MidSearch(int id)
{
System.out.println("MidSearch");
HeroTreeNode node=null;
if(left!=null)
{
node = left.MidSearch(id);
}
if(node!=null)
{
return node;
}
if(this.id==id)
{
return this;
}
if(right!=null)
{
node= right.MidSearch(id);
}
return node;
}
public HeroTreeNode PostSearch(int id)
{
System.out.println("PostSearch");
HeroTreeNode node=null;
if(left!=null)
{
node = left.PostSearch(id);
}
if(node!=null)
{
return node;
}
if(right!=null)
{
node= right.PostSearch(id);
}
if(node!=null)
{
return node;
}
if(this.id==id)
{
return this;
}
return null;
}
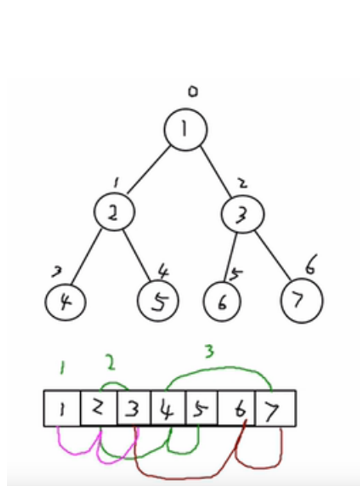
顺序存储二叉树
应用:堆排序 从数据存储来看,树的存储方式与数组的存储方式可以互相转换 二叉树的节点以数组方式存放,并且仍然可以进行前序遍历,中序遍历,和后序遍历 顺序存储二叉树的特点
- 顺序二叉树通常指考虑完全二叉树
- 第 n 个元素的左子节点为 2*n+1
- 第 n 个元素的右子节点为 2*n+2
- 第 n 元素的父节点为(n-1)/2 n 表示二叉树的第几个元素(从 0 开始)
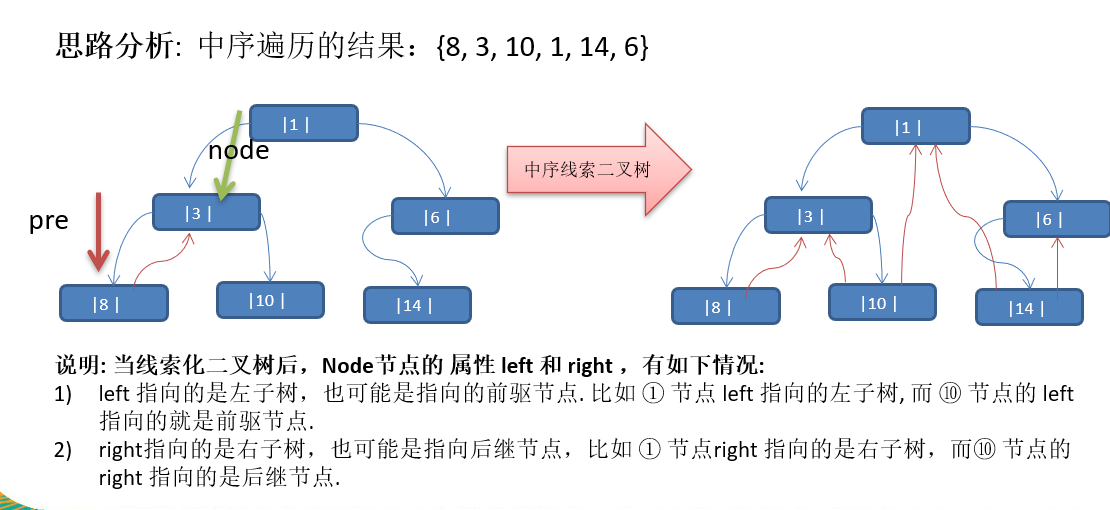
线索化二叉树
1.n 个节点的二叉链表中含有 2n-(n-1)=n+1 个空指针,利用二叉树链表中 的空指针域,存放指向节点在某种遍历顺序下的前驱和后继节点的指针 2.这种加上了线索的二叉链表称为线索链表,相应的二叉树称为线索二叉树(Threaded BinaryTree)。根据线索性质的不同,线索二叉树可分为前序线索二叉树,中序线索二叉树和后序线索二叉树三种 3.一个节点的前一个节点,称为前驱节点 4.一个节点的后一个节点,称为后继节点
优点
- 创建线索化二叉树时可以充分利用空指针域
- 通过前驱后继,可以快速索引节点,不必再次遍历
线索化二叉树以及遍历线索化二叉树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
package com.learn.tree;
public class BinaryTree
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ThreadedBinaryTree heroTree = new ThreadedBinaryTree();
//创建需要的结点
HeroTreeNode root = new HeroTreeNode(1, "tom");
HeroTreeNode node2 = new HeroTreeNode(3, "jack");
HeroTreeNode node3 = new HeroTreeNode(6, "smith");
HeroTreeNode node4 = new HeroTreeNode(8, "mary");
HeroTreeNode node5 = new HeroTreeNode(10, "king");
HeroTreeNode node6 = new HeroTreeNode(14, "dim");
//二叉树,后面我们要递归创建, 现在简单处理使用手动创建
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node2.setLeft(node4);
node2.setRight(node5);
node3.setLeft(node6);
heroTree.setRoot(root);
heroTree.Threaded();
// System.out.print(node2.leftType+" "+node2.rightType);
heroTree.ThreadedList();
// node4.ToString();
// System.out.print(node4.leftType);
// heroTree.DelNode(2);
//测试
// System.out.println("前序遍历"); // 1,2,3,5,4
// heroTree.preOrder();
//
// //测试
// System.out.println("中序遍历");
// heroTree.midOrder(); // 2,1,5,3,4
//
// System.out.println("后序遍历");
// heroTree.postOrder(); // 2,5,4,3,1
// HeroTreeNode node = heroTree.PostSearch(5);
// if(node!=null)
// {
// node.ToString();
// }else {
// System.out.println("target node is null");
// }
}
}
class HeroTree{
HeroTreeNode root;
public void setRoot(HeroTreeNode root)
{
this.root=root;
}
public void preOrder()
{
if(root!=null)
{
root.PreOrder();
}
}
public void midOrder()
{
if(root!=null)
{
root.MiddleOrder();
}
}
public void postOrder()
{
if(root!=null)
{
root.PostOrder();
}
}
//
public HeroTreeNode PreSearch(int id)
{
if(root!=null)
{
return root.PreSearch(id);
}
return null;
}
public HeroTreeNode MidSearch(int id)
{
if(root!=null)
{
return root.MidSearch(id);
}
return null;
}
public HeroTreeNode PostSearch(int id)
{
if(root!=null)
{
return root.PostSearch(id);
}
return null;
}
//删除节点
/**
* 1.如果是root则置空
* 2.判断左子节点是否是目标
* 3.判断右子节点是否是目标
* 4.1-3不满足,则递归左子节点
* 5.1-4不满足,则递归右子节点
* @param id 待删除节点
*/
public void DelNode(int id)
{
if(root==null)
{
return;
}
DelNode(root,id);
}
//删除节点
void DelNode(HeroTreeNode node,int id)
{
if(node.id==id)
{
node=null;
return;
}else if(node.left!=null && node.left.id==id)
{
node.left=null;
return;
}else if(node.right!=null&&node.right.id==id)
{
node.right=null;
return;
}
if(node.left!=null)
{
DelNode(node.left,id);
}
if(node.right!=null)
{
DelNode(node.right,id);
}
}
}
class HeroTreeNode{
public int id;
public String name;
//节点类型
public int leftType = 0;
public int rightType =0 ;
//左子节点
HeroTreeNode left;
//右子几点
HeroTreeNode right;
public void setLeft(HeroTreeNode node)
{left=node;}
public void setRight(HeroTreeNode node)
{
right=node;
}
public HeroTreeNode(int id,String name)
{
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
}
public void ToString()
{
System.out.println("id:"+id+" name:"+name);
}
/**
* 前序遍历 根节点 左节点 右节点
*/
public void PreOrder()
{
this.ToString();
if(left!=null)
{
left.PreOrder();
}
if(right!=null)
{
right.PreOrder();
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历 左节点 根节点 右节点
*/
public void MiddleOrder()
{
if(left!=null)
{
left.MiddleOrder();
}
this.ToString();
if(right!=null)
{
right.MiddleOrder();
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历 左节点 右节点 根节点
*/
public void PostOrder()
{
if(left!=null)
{
left.PostOrder();
}
if(right!=null)
{
right.PostOrder();
}
this.ToString();
}
public HeroTreeNode PreSearch(int id)
{
System.out.println("PreSearch");
if(this.id==id)
{
return this;
}
HeroTreeNode node=null;
if(left!=null)
{
node = left.PreSearch(id);
}
if(node!=null)
{
return node;
}
if(right!=null)
{
node= right.PreSearch(id);
}
return node;
}
public HeroTreeNode MidSearch(int id)
{
System.out.println("MidSearch");
HeroTreeNode node=null;
if(left!=null)
{
node = left.MidSearch(id);
}
if(node!=null)
{
return node;
}
if(this.id==id)
{
return this;
}
if(right!=null)
{
node= right.MidSearch(id);
}
return node;
}
public HeroTreeNode PostSearch(int id)
{
System.out.println("PostSearch");
HeroTreeNode node=null;
if(left!=null)
{
node = left.PostSearch(id);
}
if(node!=null)
{
return node;
}
if(right!=null)
{
node= right.PostSearch(id);
}
if(node!=null)
{
return node;
}
if(this.id==id)
{
return this;
}
return null;
}
}
//中序线索化二叉树
class ThreadedBinaryTree extends HeroTree
{
HeroTreeNode pre=null;
public void Threaded()
{
Threaded(root);
}
public void Threaded(HeroTreeNode node)
{
if(node==null)
{
return;
}
Threaded(node.left);
//线索化前驱节点
if(node.left==null)
{
node.left=pre;
//指定type
node.leftType=1;
}
if(pre!=null && pre.right==null)
{
pre.right=node;
pre.rightType=1;
}
pre=node;
Threaded(node.right);
}
public void ThreadedList()
{
HeroTreeNode node = root;
while(node != null) {
//循环的找到leftType == 1的结点,第一个找到就是8结点
//后面随着遍历而变化,因为当leftType==1时,说明该结点是按照线索化
//处理后的有效结点
while(node.leftType == 0) {
node = node.left;
}
//打印当前这个结点
node.ToString();
//如果当前结点的右指针指向的是后继结点,就一直输出
while(node.rightType == 1) {
//获取到当前结点的后继结点
node = node.right;
node.ToString();
}
//替换这个遍历的结点
node = node.right;
}
}
}
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权