shader入门基础-高级纹理
shader入门基础-高级纹理
本文内容主要参考 《Unity shader 入门精要》一书,旨在总结所学知识与加深个人理解
立方体纹理(Cubemap)
立方体纹理一共包含了 6 张图像,这些图像对应了一个立方体的 6 个面,立方体纹理的名称也由此而来。立方体纹理是环境映射(Environment Mapping)的一种实现方法。
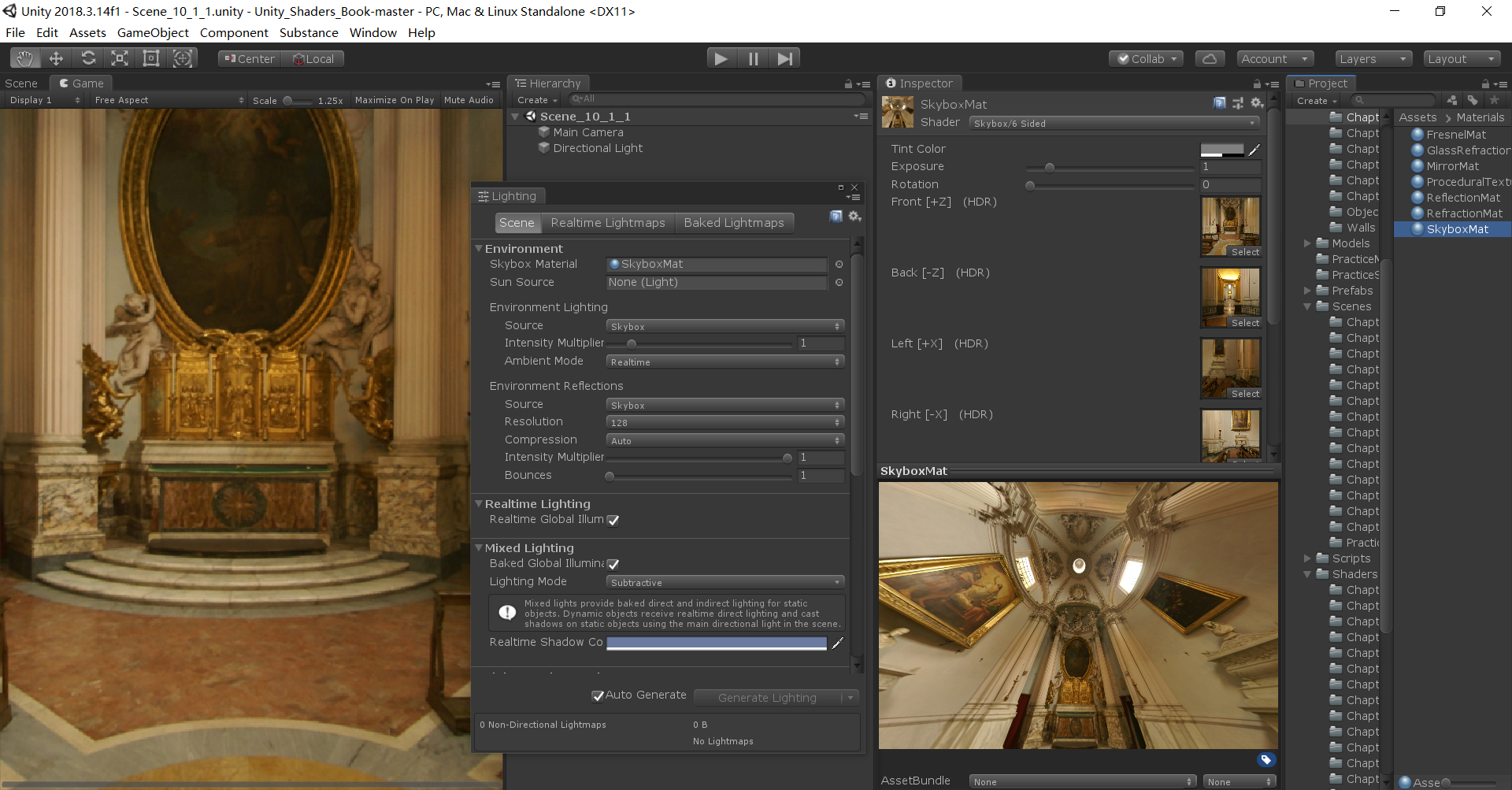
天空盒
- shader 使用 Skybox/6 Sided,需要 6 张纹理
- 纹理的 wrap mode 设置为 Clamp,以防止在接缝处出现不匹配的现象
- 保证渲染场景的摄像机的 Camera 组件 Clear Flags 被设置为 Skybox
天空盒设置如图
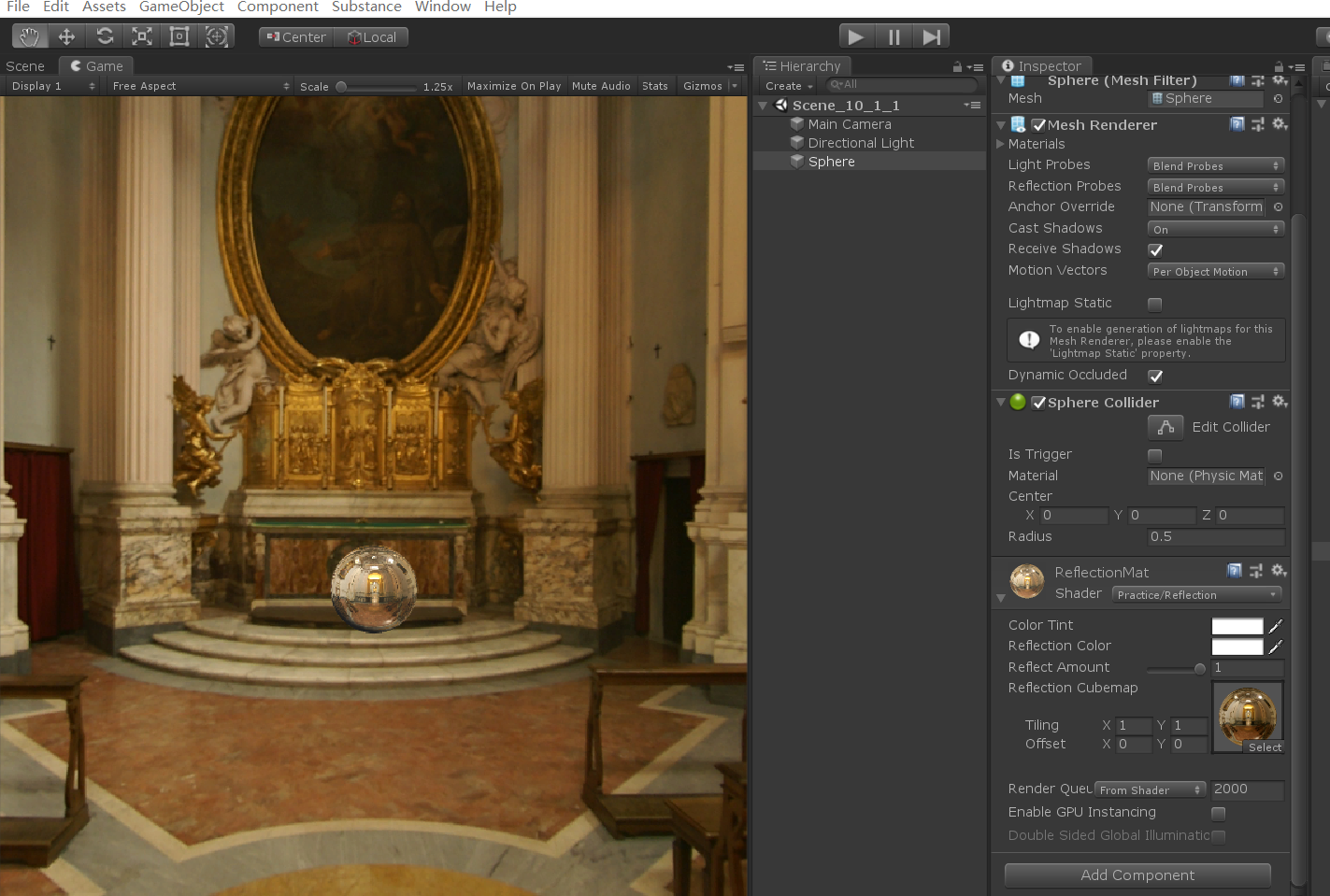
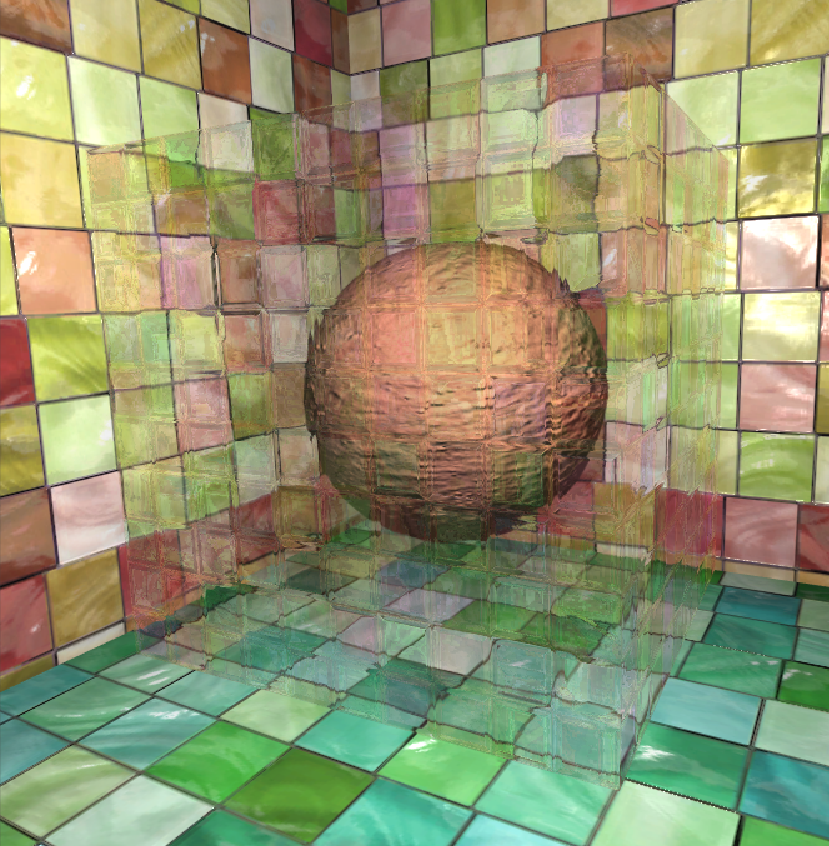
反射
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
//反射
Shader "Practice/Reflection" {
Properties {
_Color ("Color Tint", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_ReflectColor ("Reflection Color", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_ReflectAmount ("Reflect Amount", Range(0, 1)) = 1
//立方体纹理进行采样
_Cubemap ("Reflection Cubemap", Cube) = "_Skybox" {}
}
SubShader {
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" "Queue"="Geometry"}
Pass {
Tags { "LightMode"="ForwardBase" }
CGPROGRAM
#pragma multi_compile_fwdbase
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "Lighting.cginc"
#include "AutoLight.cginc"
fixed4 _Color;
fixed4 _ReflectColor;
fixed _ReflectAmount;
samplerCUBE _Cubemap;
struct a2v {
//使用阴影计算的宏,必须用vertex
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
};
struct v2f {
//使用阴影计算的宏,必须用pos
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float3 worldPos : TEXCOORD0;
fixed3 worldNormal : TEXCOORD1;
fixed3 worldViewDir : TEXCOORD2;
fixed3 worldRefl : TEXCOORD3;
SHADOW_COORDS(4)
};
v2f vert(a2v v) {
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal);
o.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz;
o.worldViewDir = UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(o.worldPos);
// 计算 反射方向
o.worldRefl = reflect(-o.worldViewDir, o.worldNormal);
TRANSFER_SHADOW(o);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target {
fixed3 worldNormal = normalize(i.worldNormal);
fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(i.worldPos));
fixed3 worldViewDir = normalize(i.worldViewDir);
//环境光
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz;
////C_diffuse = (C_light·m_diffuse)max(0,N·L) //漫反射计算公式
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Color.rgb * max(0, dot(worldNormal, worldLightDir));
//texCUBE 对立方体纹理进行采样
fixed3 reflection = texCUBE(_Cubemap, i.worldRefl).rgb * _ReflectColor.rgb;
UNITY_LIGHT_ATTENUATION(atten, i, i.worldPos);
// Mix the diffuse color with the reflected color
//混合漫反射和反射颜色等价于
//float lerp(float a, float b, float w) {
//return a(1-w) + b * w;
//}
//混合后 阴影值与漫反射和反射颜色值相乘
fixed3 color = ambient + lerp(diffuse, reflection, _ReflectAmount) * atten;
return fixed4(color, 1.0);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Reflective/VertexLit"
}
折射
斯涅耳定律 \(\eta_1sin\theta_1=\eta_2sin\theta_2\) \(\eta_1和\eta_2\) 是兩個介質的折射率。
refract 第一个参数是入射光线的方向,它必须是归一化后的矢量;第二个参数是表面法线,法线方向同样需要是归一化后的,第三个参数是入射光线 所在介质的折射率和折射光线所在介质的折射率之间的比值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
//折射
Shader "Practice/Refract"
{
Properties
{
_Color ("Color Tint", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_RefractColor("折射顏色",Color)=(1,1,1,1)
_RefractAmount("折射程度",Range(0,1))=1
//入射光線所在介質的折射率和折射光線所在介質的折射率之間的比值
_RefractRatio("折射率比值",Range(0.1,1))=0.5
//环境映射的立方体纹理
_Cubemap("环境映射",Cube)="_Skybox"{}
}
SubShader
{
// No culling or depth
Tags{"RenderType"="Opaque" "Queue"="Geometry"}
Pass
{
Tags{"LightModel"="ForwardBase"}
CGPROGRAM
#pragma multi_compile_fwdbase
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "Lighting.cginc"
#include "AutoLight.cginc"
fixed4 _Color;
fixed4 _RefractColor;
float _RefractAmount;
fixed _RefractRatio;
samplerCUBE _Cubemap;
struct a2v {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
};
struct v2f {
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float3 worldPos : TEXCOORD0;
fixed3 worldNormal : TEXCOORD1;
fixed3 worldViewDir : TEXCOORD2;
fixed3 worldRefr : TEXCOORD3;
SHADOW_COORDS(4)
};
v2f vert(a2v v) {
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal);
o.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz;
o.worldViewDir = UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(o.worldPos);
//第一个参数是入射光线的方向,它必须是归一化后的矢量;第二个参数是表面法线,法线方向同样需要是归一化后的,第三个参数是入射光线
//所在介质的折射率和折射光线所在介质的折射率之间的比值。
o.worldRefr = refract(-normalize(o.worldViewDir), normalize(o.worldNormal), _RefractRatio);
TRANSFER_SHADOW(o);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target {
fixed3 worldNormal = normalize(i.worldNormal);
fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(i.worldPos));
fixed3 worldViewDir = normalize(i.worldViewDir);
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz;
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Color.rgb * max(0, dot(worldNormal, worldLightDir));
// Use the refract dir in world space to access the cubemap
fixed3 refraction = texCUBE(_Cubemap, i.worldRefr).rgb * _RefractColor.rgb;
UNITY_LIGHT_ATTENUATION(atten, i, i.worldPos);
// Mix the diffuse color with the refract color
fixed3 color = ambient + lerp(diffuse, refraction, _RefractAmount) * atten;
return fixed4(color, 1.0);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Reflective/VertexLit"
}
菲涅尔反射
菲涅尔反射描述了一种光学现象,即当光线照射到物体表面上是,一部分发生反射,一部分进入物体内部,发生折射或散射。
菲涅尔近等式: \(F_{schlick(\vec v,\vec n)} = F_0+(1-F_0)*(1-\vec v \cdot \vec n)^5\)
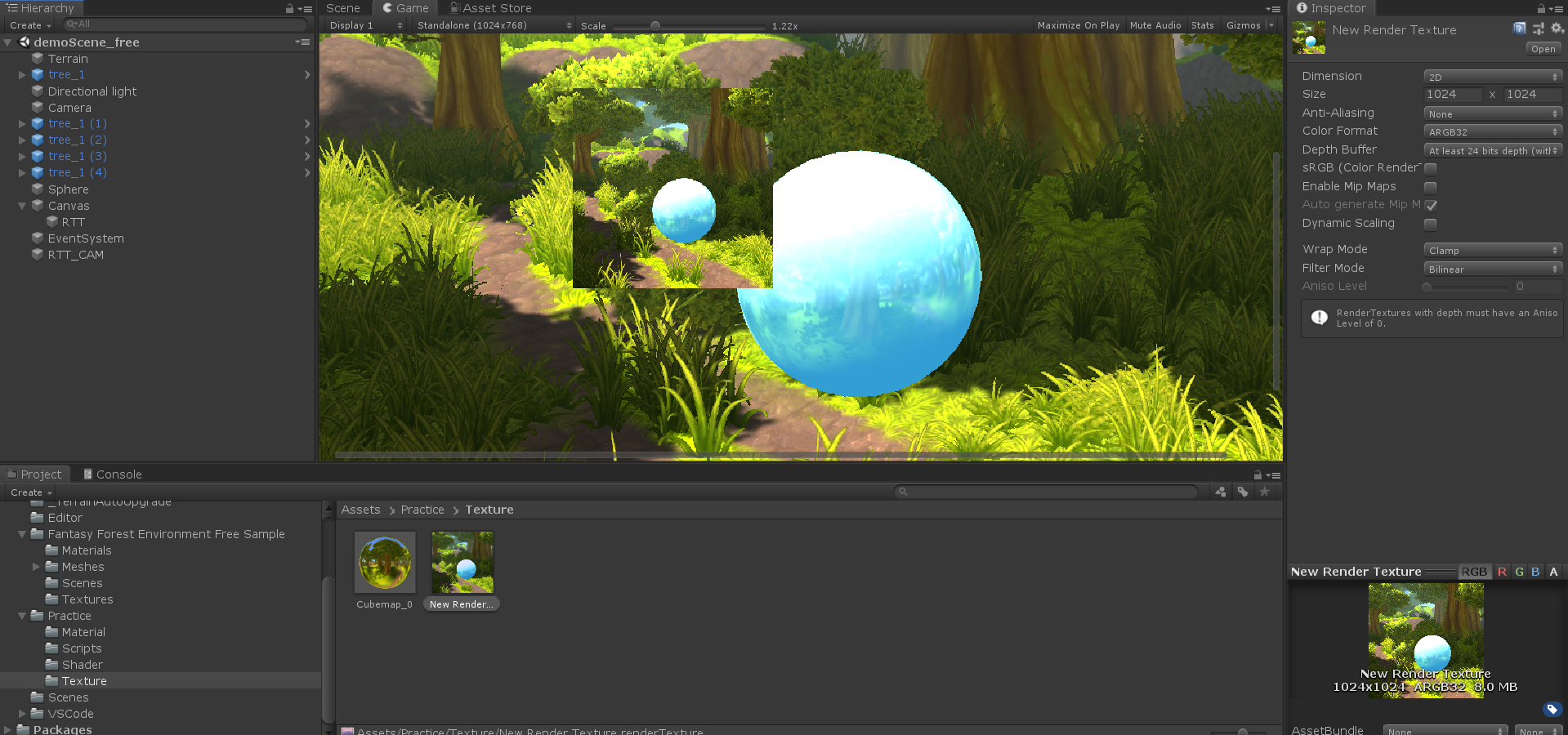
渲染纹理
渲染目标纹理(Render Target Texture,RTT) GPU 允许把整个三维场景渲染到一个中间缓冲中。 多重渲染目标纹理(Multiple Render Target,MRT) GPU 允许我们把场景同事渲染到多个渲染目标纹理中,而不再需要为每个渲染目标纹理单独渲染完整的场景。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
//渲染目标物理
Shader "Practice/RTT"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
}
SubShader
{
Tags {"RenderType"="Opaque" "Queue"="Geometry"}
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
struct a2v
{
float4 vertex:POSITION;
float3 texcoord:TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
};
v2f vert (a2v v)
{
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord,_MainTex);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
fixed4 col = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv);
return col;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
GrabPass
一种特殊的 Pass 来获取屏幕图像的目的。通常使用 GrabPass 来实现诸如玻璃等透明材质的模拟,与使用简单透明混合不同,使用 GrabPass 可以让我们对该物体后面的图像进行更浮渣的处理,例如使用法线来模拟折射效果,而不再是简单的和原屏幕颜色进行混合。
Grab 支持的两种形式:
- 直接使用 GrabPass{},然后在后续的 Pass 中直接使用_GrabTexture 来访问屏幕图像。但是,当场景中有多个物体都使用了这样的形式抓取屏幕是,这种 方法的性能消耗比较大,因为对于每一个使用它的物体,Unity 都会为他单独进行一次昂贵的屏幕抓取操作。但这种方法可以让每个物体得到不同的屏幕图像,这取决于它们的渲染队列及渲染它们当时当前屏幕缓冲中的颜色。
- 使用 GrabPass{“TextureName”},Unity 只会在每一帧时为第一个使用名为 TextureName 的纹理的物体执行一次抓取屏幕的操作,而这个纹理同样可以在其他 Pass 中被访问。这种消耗更小。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
Shader "Practice/GlassRefraction" {
Properties {
//该玻璃材质纹理
_MainTex ("Main Tex", 2D) = "white" {}
//该玻璃法线纹理
_BumpMap ("Normal Map", 2D) = "bump" {}
//模拟反射所用的环境纹理
_Cubemap ("Environment Cubemap", Cube) = "_Skybox" {}
//用于控制模拟折射时图像的扭曲程度
_Distortion ("Distortion", Range(0, 100)) = 10
//用于控制折射程度,0则不会发生折射,只有反射,1则只有反射没有折射
_RefractAmount ("Refract Amount", Range(0.0, 1.0)) = 1.0
}
SubShader {
// 保证不透明物体先进行渲染.
Tags { "Queue"="Transparent" "RenderType"="Opaque" }
GrabPass { "_RefractionTex" }
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
sampler2D _BumpMap;
float4 _BumpMap_ST;
samplerCUBE _Cubemap;
float _Distortion;
fixed _RefractAmount;
//GrabPass指定的纹理名称
sampler2D _RefractionTex;
//纹理纹素大小
float4 _RefractionTex_TexelSize;
struct a2v {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float4 tangent : TANGENT;
float2 texcoord: TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float4 scrPos : TEXCOORD0;
float4 uv : TEXCOORD1;
float4 TtoW0 : TEXCOORD2;
float4 TtoW1 : TEXCOORD3;
float4 TtoW2 : TEXCOORD4;
};
v2f vert (a2v v) {
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.scrPos = ComputeGrabScreenPos(o.pos);
o.uv.xy = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _MainTex);
o.uv.zw = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _BumpMap);
float3 worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz;
fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal);
fixed3 worldTangent = UnityObjectToWorldDir(v.tangent.xyz);
fixed3 worldBinormal = cross(worldNormal, worldTangent) * v.tangent.w;
o.TtoW0 = float4(worldTangent.x, worldBinormal.x, worldNormal.x, worldPos.x);
o.TtoW1 = float4(worldTangent.y, worldBinormal.y, worldNormal.y, worldPos.y);
o.TtoW2 = float4(worldTangent.z, worldBinormal.z, worldNormal.z, worldPos.z);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target {
float3 worldPos = float3(i.TtoW0.w, i.TtoW1.w, i.TtoW2.w);
fixed3 worldViewDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(worldPos));
// Get the normal in tangent space
fixed3 bump = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, i.uv.zw));
// Compute the offset in tangent space
float2 offset = bump.xy * _Distortion * _RefractionTex_TexelSize.xy;
i.scrPos.xy = offset * i.scrPos.z + i.scrPos.xy;
fixed3 refrCol = tex2D(_RefractionTex, i.scrPos.xy/i.scrPos.w).rgb;
// Convert the normal to world space
bump = normalize(half3(dot(i.TtoW0.xyz, bump), dot(i.TtoW1.xyz, bump), dot(i.TtoW2.xyz, bump)));
fixed3 reflDir = reflect(-worldViewDir, bump);
fixed4 texColor = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv.xy);
fixed3 reflCol = texCUBE(_Cubemap, reflDir).rgb * texColor.rgb;
fixed3 finalColor = reflCol * (1 - _RefractAmount) + refrCol * _RefractAmount;
return fixed4(finalColor, 1);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Diffuse"
}
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权